eCommerce fraud has been around for years, but it has surged recently with the rise of online shopping. Cybercriminals exploit the vast amount of payment card data and personally identifiable information stored by eCommerce platforms, using various tactics to gain unauthorized access.
This article examines the growing threat of eCommerce fraud, emphasizing why businesses must recognize and combat it with effective prevention strategies.
eCommerce fraud happens when someone uses dishonest tactics to make unauthorized purchases or steal financial information on an online store.
These fraudulent activities include unauthorized use of payment information, identity theft, account takeovers, and chargeback fraud. In 2024, global eCommerce fraud losses are projected to reach $44.3 billion, with forecasts indicating a rise to $107 billion by 2029.
Fraudulent transactions usually display patterns that differ from real ordering, and merchants should be wary of new customers placing high-value orders back-to-back; bulk orders that include risk items such as electronics or luxury gift cards. To resell these items for money quickly, fraud perpetrators tend to wall up and draw waiting victims into their final traps.
The sudden change in order history from little to high dollar values may indicate fraud. Alerts for those anomalies can be configured automatically within a business so that suspicious activity can occur long before the transaction is processed.
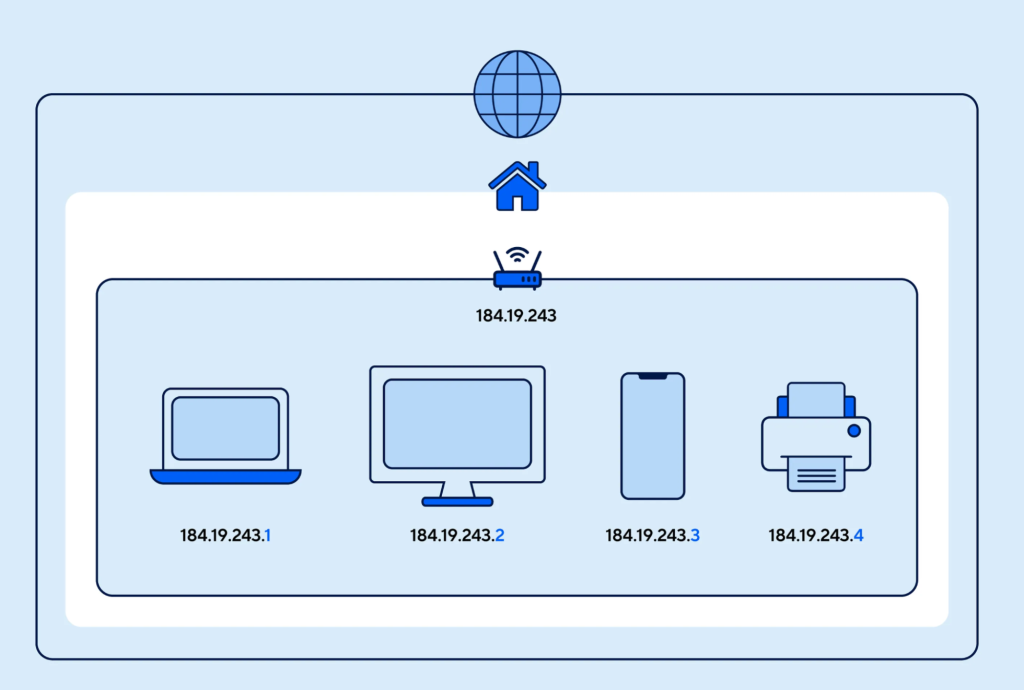
Tracking IP address and device information of the customer indicates fresh fraud tries. Transactions from high-risk countries, proxies, or VPN IP addresses should mainly be scrutinized because they hide venues of fraudsters at their real location.
A very strong hint of fraud activity is when most orders are placed from the same device but paid for with a completely different account. Businesses would then put up IP fraud scoring tools to capture suspicious logins and purchases so that a high-risk transaction would be blocked or require extra verification steps.
Mismatches between billing and shipping addresses are a frequent occurrence in fraudulent transactions. While some instances may be genuine, for example, customers may order gifts for recipients in other countries; nevertheless, orders with shipping addresses in different countries from the billing addresses warrant more scrutiny.
Additionally, invalid or incomplete addresses, followed by multiple payment methods on the same account almost instantaneously, are some things that should warn the merchant. Monitoring these aspects may be achieved by integrating Address Verification Service (AVS) and giving extra scrutiny to any transactions in which the key details do not match.
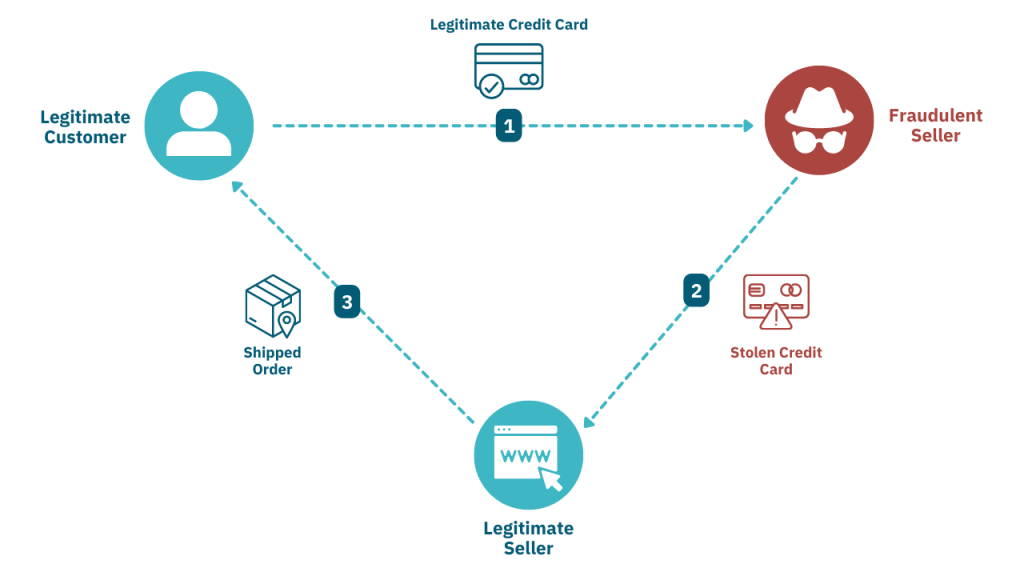
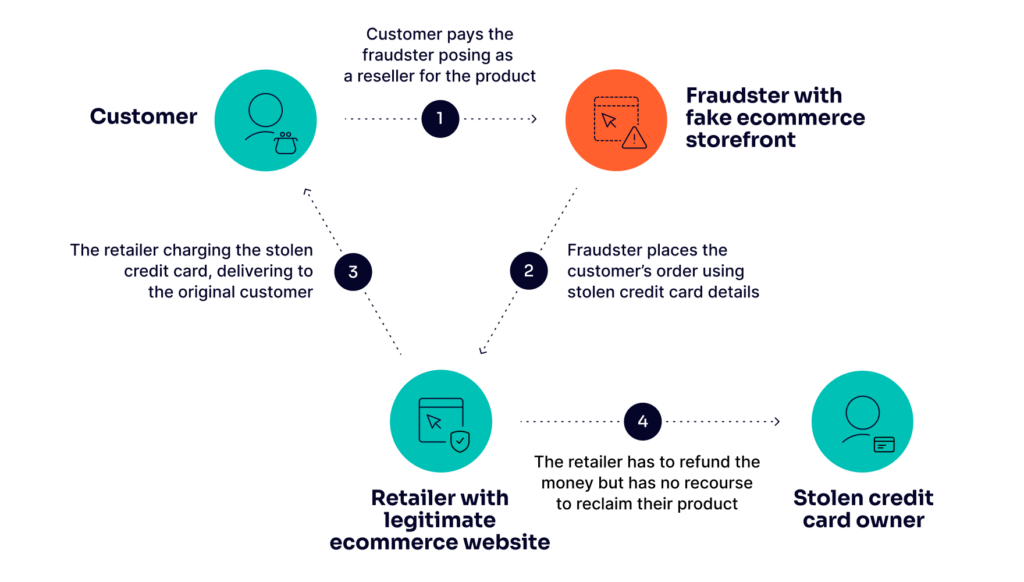
Triangulation fraud is a very advanced form of scam in which the fraudster sets up a website or marketplace listing to dupe naive consumers into purchasing products on the false site.
How It Works:
A fraudster creates an online store or sells items on eBay, offering goods at very low prices so as to attract buyers.
When a customer orders, the fraudster uses stolen credit card details to purchase the product from a legitimate retailer and have it shipped directly to the buyer.
Thus, while the customer receives the item, he is oblivious of the fraud; meanwhile, the actual cardholder, whose details were stolen, notices the unauthorized charges and files a chargeback.
Return fraud occurs when a customer illegitimately takes advantage of a store’s return policy for profit.
How It Works:
A fraudster might return a product he or she stole in order to get a refund.
Someone may purchase an expensive product, use it for one or two occasions, and then return it, claiming it was never used (this is called “wardrobing”).
Genuine products are replaced with a fake or damaged product before returning.
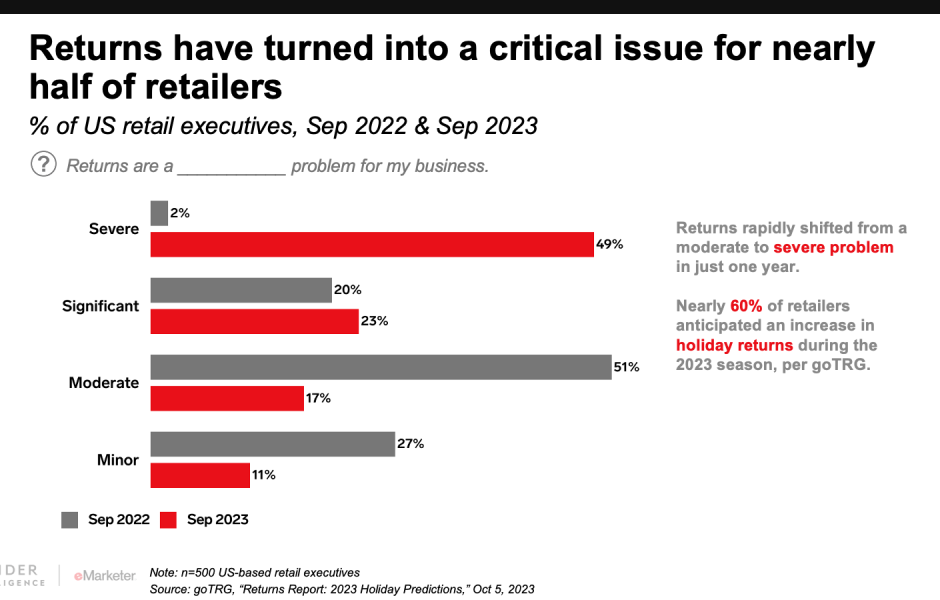
Source: eMarketer
Account Takeover fraud is done by cybercriminals gaining unauthorized access to a customer account to obtain financial benefit. The major concern with this type of fraud is that it is difficult to detect since fraudsters often hide their tracks.
How It Works:
A fraudster steals the login credentials from victims using a phishing email, data breach, or malware.
They then change the password to prevent the real owner from regaining access to his or her account.
They then use the stored payment method in the victim’s account to make unauthorized purchases, redeem loyalty points, or withdraw funds from the account.
Fraudsters often change the shipping address, so the items are delivered directly to them.
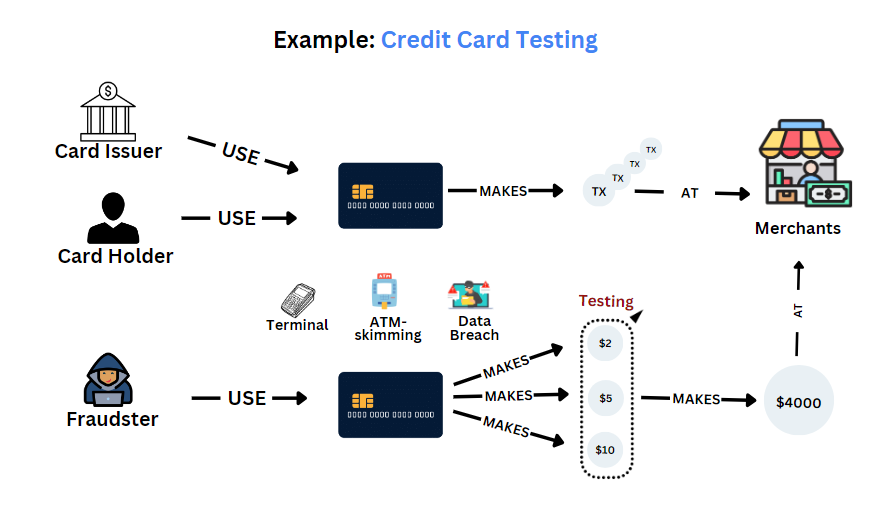
The name “card testing” explains that the fraudsters, after obtaining stolen credit cards, try to test them with smaller purchases before going on with bigger ones. These disturbances are usually unnoticed until the victim notices a lot of unrecognized charges on their statement.
How It Works:
A fraudster obtains stolen card numbers from a data breach or from the dark web.
The fraudster processes a number of minimal-value transactions (eg. $1 or under), thus verifying if the card is active.
After validation, the fraudster will proceed with big purchases using the card or sell the validated card details.
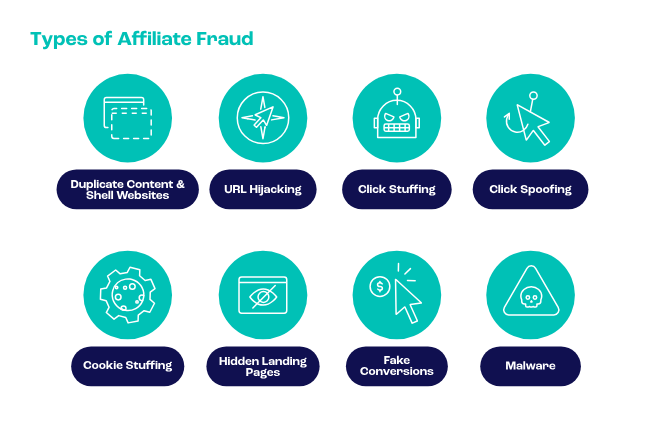
Affiliate fraud occurs when fraudsters exploit the eCommerce affiliate program to manipulate it in such a way to convert fake traffic, fraudulent transactions, or stolen payment details into undeserved commissions.
How It Works:
Some fraudsters set up an automated bot that generates fake clicks and leads to appear to be bringing in real shoppers.
Others would use stolen credit card information to simulate an authentic purchase allowing the system to pay them their commissions.
In some instances, they hijack other affiliates’ links and steal their commissions from other marketers.
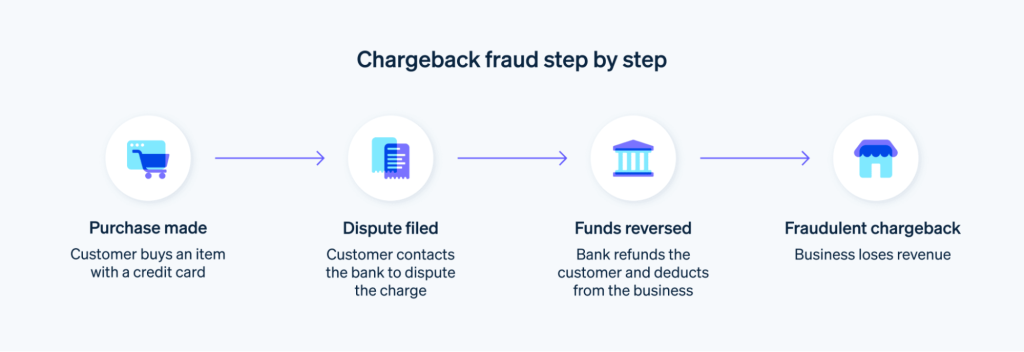
Chargeback fraud occurs when a customer misrepresents a legitimate transaction wherein a purchase is legitimately made and empties a bank after getting hold of a product.
How It Works:
A customer purchases an item and gets it. Later they tell their bank the activity was unauthorized, or they never received it.
The bank will issue a chargeback and refund to the consumer while reversing the transaction.
The retailer loses the product and the payment while being charged for the chargeback.
Identity theft tends to happen on the Internet when a fraudster uses his illegally obtained information to make unauthorized purchases, apply for a store credit, or commit financial fraud in somebody else’s name.
How It Works:
Hackers steal personal details from phishing scams, malware, or large-scale data breaches.
This stolen information is then used to make purchases or open accounts, and request financial services.
The victim often discovers the fraud when he is reviewing bank statements or receives unexpected bills.
Interception fraud occurs when a fraudulent person orders stolen payment details and manipulates the shipping to intercept the delivery package before the real cardholder knows.
How It Works:
The fraudster makes an order using a stolen credit card and using the real cardholder’s billing address to avoid suspicion since they affirm the order.
After that, they call customer service or the shipment carrier and reroute the package to another address.
Generally, by the time the real cardholder disputes the charge, the fraudster has already taken possession of the goods.
Credit card fraud happens when a fraudster uses stolen or illegally obtained credit card details without a knowledge purchaser to commit an unauthorized transaction. This is one of the most common online shopping frauds and affects both businesses and consumers.
How It Works:
A fraudster obtains the stolen credit card details by phishing, hacking, or selling it from dark webs.
After that, they use the stolen card information for online purchases which the cardholder does not know about.
The cardholder notices the transactions after some time and will report the case to the bank leading to a chargeback which the merchant needs to pay.
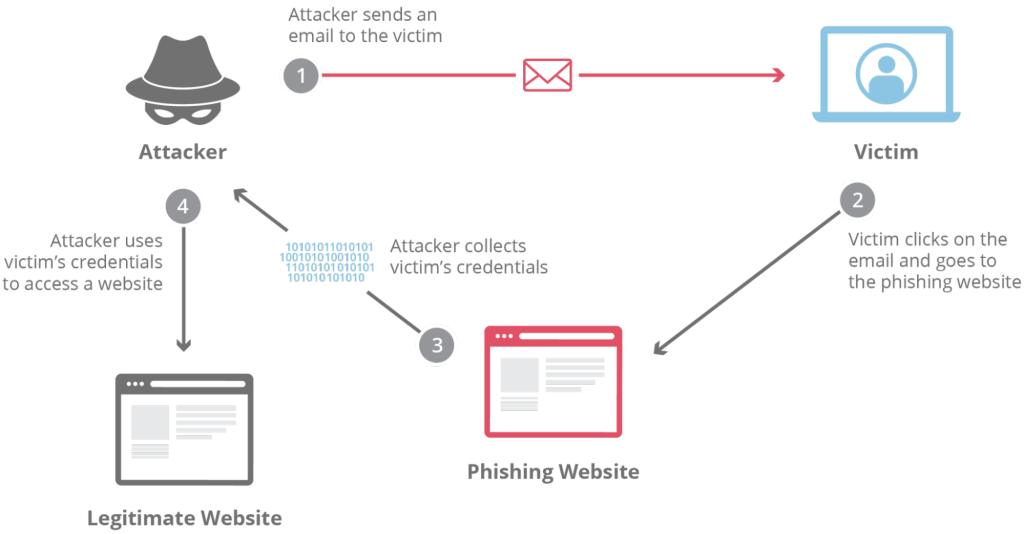
Phishing is a fraudulent tactic, associated with scamming victims into revealing personal and financial information by assuming the identity or behavior of a legitimate organization such as a bank or an eCommerce website.
How It Works:
Fraudsters send emails or messages or give fake log-ins which look exactly as that of a trusted retailer or payment provider.
Victims often punch in their Login credentials, credit card numbers, or any other information unknowingly feeding it to the fraudster.
And the unfortunate name outside the crime is used by the fraud to make purchases with this information on stealing or access accounts.
Coupon, gift card, and promo code abuse happen when people exploit loopholes to get unauthorized discounts or benefits. Fraudsters may use fake accounts, stolen codes, or bots to claim multiple promo offers meant for single use.
One major type is gift card fraud, where criminals steal or manipulate balances for purchases or resale. Since many platforms don’t require identity verification, gift cards are an easy target. Some fraudsters even use stolen credit cards to buy gift cards and convert them into cash.
How It Works:
Fraudsters steal gift card numbers by hacking into the retailer’s databases and use bots to try out random card numbers.
Some identity thieves buy stolen gift cards and acquire them at a discount for online shopping.
Some may ask refunds in the form of the gift card instead of hard cash and then sell them on the secondary markets.
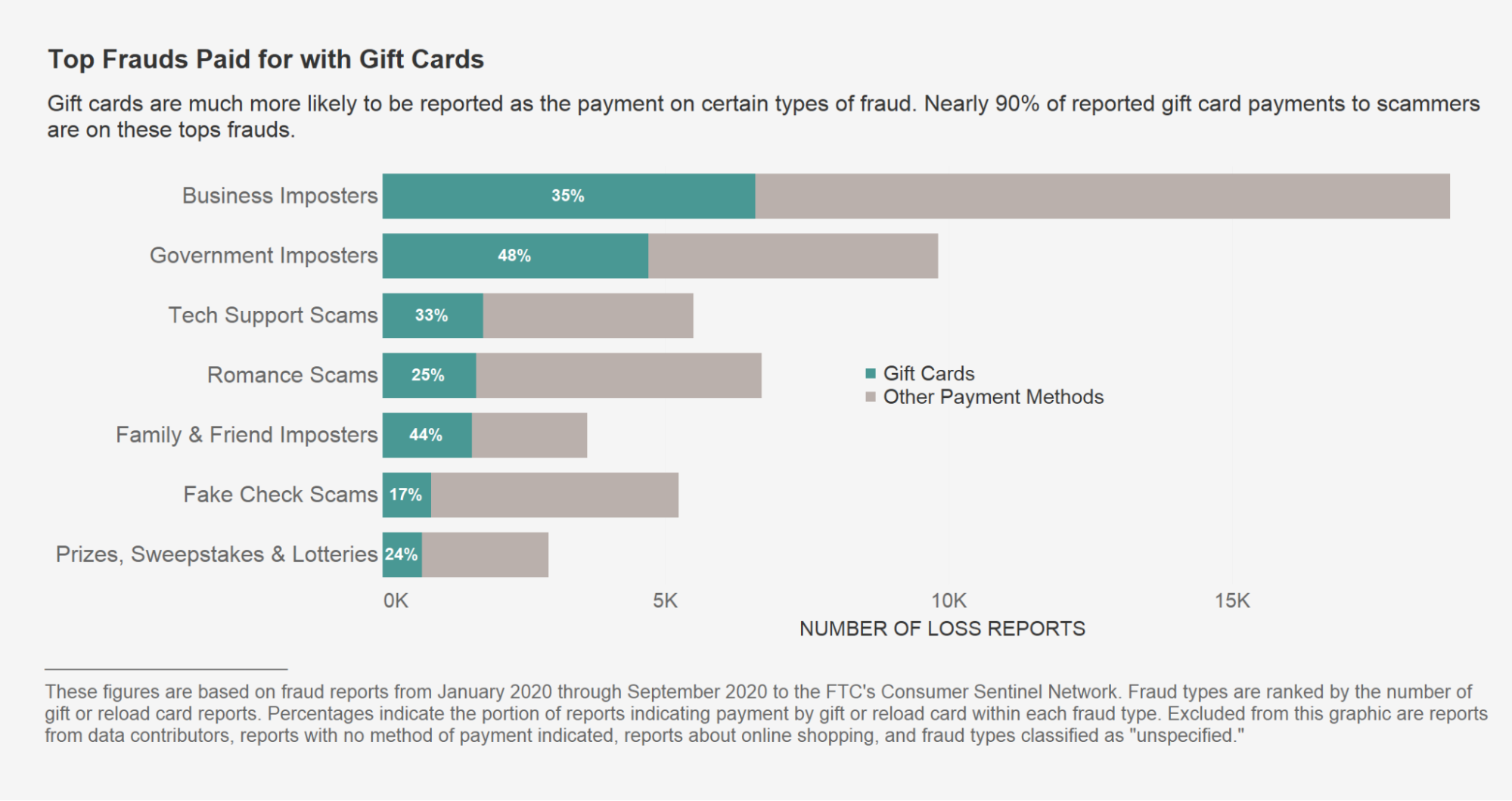
Source: Federal Trade Commission
eCommerce fraud rates are continually increasing, and robust measures should be put in place to secure revenue at all costs and protect potential and returning customers alike. Here are some of the most effective e-commerce fraud prevention measures:
IP fraud scoring tools examine a customer’s IP address to determine if suspicious activities are taking place and assess the risk level of a transaction. For instance, it identifies fraud by investigating presence of geolocation mismatches, proxy or VPN use, and any history of fraud associated with the IP address.
An organization could employ an automated fraud detection program to generate a risk score for every transaction. A transaction tagged with high risk may be subject to manual review or declined outright. Using IP fraud scoring coupled with real-time transaction monitoring, merchants can work toward minimizing the amounts of unauthorized purchases and chargebacks.
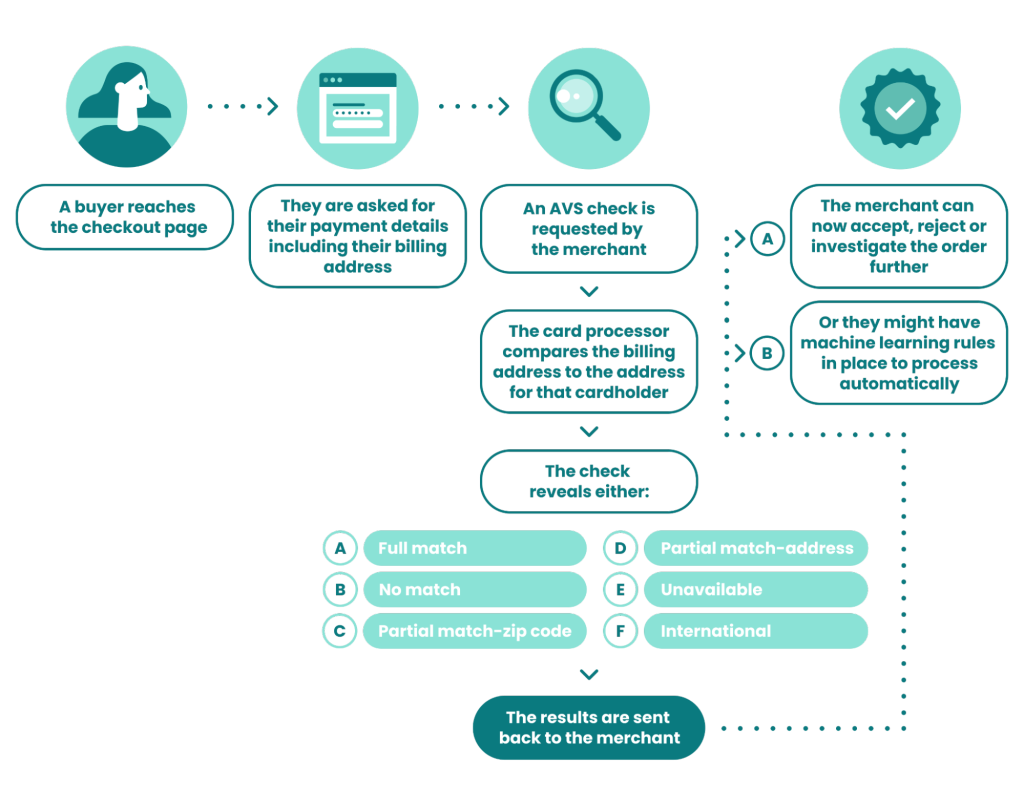
AVS is part of the fraud detection software that verifies the billing address the customer gives against the one on file with the credit card issuer. When they do not match, the transaction is either flagged or declined.
Merchants can configure their payment processing systems to decline based on full AVS mismatch or require different verification steps. This will help prevent the unauthorized usage of credit cards, hence preventing such cases of chargebacks because the card has been stolen.
Most fraudulent purchasers will stock-pile expensive items while getting away with it before the scam is detected. The business could, therefore, limit the number of purchases on certain value items or specify order quantity per transaction.
Limits such as those above, with a maximum per order, per customer, or restricting initial purchases of high-risk items have the potential of discouraging fraud attempts. Another is monitoring unusual orders, for example, frequent orders of large quantities from a single IP address or device.
Strengthening authentication makes possible a considerable reduction of fraud tendencies by inhibiting access to customer accounts and details of payment without authorization. Implicitly, two-factor authentication (2FA), multi-factor authentication (MFA), meaning requiring the user to verify identity through one or more of these mediums: a one-time password (OTP), a biometric authentication, or a security question.
For example, a merchant will have strict 2FA requirements for account logins, particularly, if the user will seek sensitive information or make purchases of large value. Further strengthening the security should make suggestions to customers about requiring strong, unique passwords and monitoring sign-in attempts from unknown devices or locations.
It’s the newest trick under the sleeve added by businesses for staying ahead of fraudulent activities. These systems are programmed to analyze user behavior, keep track of transaction history, and monitor the device fingerprints so that anything presenting a reddish flag can be made before a purchase goes in. All these bring several solutions into existence, with each putting up different guards against the intruder.
Blockify App is an excellent example of how fraud can be prevented via disabling high-risk IPs, bot detection, and preventing unauthorized access to eCommerce-entry points.
All above are useful in terms of automated security as this has helped to filter out bad traffic and poses great promise in fraud detection and verification strategies. Having a single tool like Blockify in your security stack will prevent fraud even before it starts.
Final Thoughts
eCommerce fraud is constantly evolving, making proactive prevention essential. By understanding fraud types, using detection tools, and enforcing security measures like IP fraud scoring and multi-factor authentication, businesses can minimize risks. Protecting your store not only prevents financial losses but also builds customer trust, ensuring a secure and successful eCommerce operation.